INTRODUCTION TO INDUSTRIAL IOT
The Internet has transformed how people communicate, what they do, and how they work together. Now, the Internet is doing the same for machines. In the past few years, equipment manufacturers have focused on interconnecting automation systems. These connected systems make up what is called the Industrial IoT (IIoT).
Industry 4.0 is the latest evolution in industrial automation history and it is affecting all industries. Not only is the pace of change accelerating, but so are the technological leaps. In the next few years, engineers in all industries are going to find a way to leverage the new capabilities generated by connecting machines and processes with more powerful computational and analytical capabilities.
Machines are an integral part of any manufacturing or processing industry, and with IIoT, machines can now send live data about how they are performing and allow remote servicing if needed.
PROCECO has implemented IIoT into its wastewater treatment equipment (Éco-Smart®). The Éco-Smart® uses mechanical vapor recompression to separate water from diluted wastewater that contains oil, dissolved solids, and metals. To learn more about the advantages of the PROCECO Éco-Smart®, visit our website.
COMPONENTS OF IIOT
IIoT networks are divided into four levels: monitoring, network, service, and application. Each of these levels deploys different components in order to carry out tasks. The monitoring level consists of appliances such as RFID tags, BLE devices, sensors, etc. These components monitor the physical state and operational condition of the equipment. The Éco-Smart® uses a multitude of sensors to monitor the temperature, flow, and pressure of operation.
This information is gathered by the PLC, which generates data and uses a gateway to send the information to the network level. The network protocols used depend on a number of factors. The most common are Wi-Fi, cellular (4G, 5G), local Ethernet (hardwire), or Cloud-based networks.
The service and application levels include software for database management, API services, etc. This allows the data collected to be accessed by multiple tools and software for analysis and reporting.
BENEFITS OF IIOT IN MANUFACTURING
REMOTE MONITORING (DASHBOARD)
One of the main advantages of the IIoT is the ability to view the condition of equipment from anywhere and at any given time. The data collected from the sensors can easily be reported to a dashboard, which consists of a digital representation of the physical equipment and highlights the key parameters of equipment operation and status. The PROCECO Connect® interface used for the Éco-Smart® allows authenticated users to easily review the status of the equipment from a computer or mobile device.
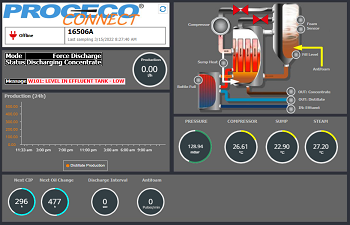
PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE (REDUCED MAINTENANCE COST)
Traditionally, manufacturer recommendations and maintenance team experiences provided the basis for maintenance plans. Routine inspections might detect a noisy bearing or decrease in production before an equipment failure occurs. The maintenance team plans for corrective actions, hopefully before a breakdown occurs, which would force emergency measures to be implemented.
With IIoT, the data collected is analyzed to monitor machine operating conditions in real-time and allow the detection of equipment issues at an early stage, providing more flexibility to schedule a maintenance intervention and reducing costly operation downtime.
For example, the PROCECO Éco-Smart® uses IIoT to trigger notifications whenever maintenance will soon be required, allowing the maintenance team to schedule it at their convenience and avoid interruption during production hours. Some maintenance operations can also be triggered remotely, such as leak testing and cleaning-in-place cycles.
INCREASED PRODUCTIVITY, QUALITY, & PERFORMANCE
With IIoT, the status of equipment is continuously monitored and adjustments can be made in real-time to optimize production.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used to implement corrective actions on the equipment, based on analyzed data to maintain equipment at its optimum capacity. AI can also help in troubleshooting equipment malfunctions. For example, AI can detect a reduction in Éco-Smart® production and trigger a cleaning-in-place cycle during production shutdown. Should that not resolve the issue, the system could guide the maintenance team in performing tests to correct the issue.
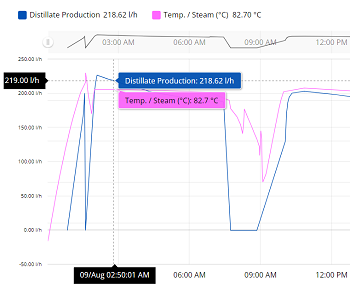
MONITOR THE CONSUMPTION OF RESOURCES
Companies can use IIoT to monitor the consumption of resources (water, cleaning solution, power, etc.) and to generate reports to evaluate resource requirements. This way, the process team can gain a clearer understanding of the process and its performance, and avoid shortages or production shutdowns.
CHALLENGES OF IIOT ADOPTION
RETURN ON INVESTMENT
Measuring ROI on IIoT initiatives can be very complex. In fact, a survey conducted in 2019 by Harvard Business Review Analytics showed that only 10% of their respondents could accurately measure ROIs for their IoT initiatives. This does not mean that there are none, but rather that ROIs could be difficult to measure.
Many factors have to be considered when evaluating the ROI on an IIoT project. RFID tags and BLE devices and sensors are not expensive, but the cost of network and cybersecurity implementations can be significant.
Therefore, when starting any IIoT project, it is important to identify the problems that need to be resolved. For example, you may not need to connect all the sensors and track all the machine operations.
DATA SECURITY
All levels of the IIoT could be exposed to different cybersecurity threats. RFID tags and BLE devices and sensors can be hacked locally. The network integrity may be disrupted by cyberattacks or rerouted, which would allow data to be falsified, deleted, or stolen. Any malicious access to a network poses a threat to corporate information.
Cybersecurity must be a factor in the early stages of IIoT strategy development. Help and support from cybersecurity professionals should be carefully considered. A proactive cybersecurity plan is often a small investment compared to the cost of repairing the damage caused by a security breach.
CONCLUSION
The Industrial Internet of Things has a bright and shiny future. By embedding connected devices into machines, companies are able to improve existing operations, as well as produce ones that are more effective. IIoT allows users to gain a quick understanding of their operations. With all of the expected benefits, it is safe to say that IIoT will continue to have a great impact on production efficiency.



